Optimize Workforce Planning using Linear Programming with Python
What is the minimum number of temporary workers you need to hire to absorb your weekly workload while ensuring employees retention?

A significant challenge faced by Distribution Centre (DC) managers is the fluctuation of the workload during the week.
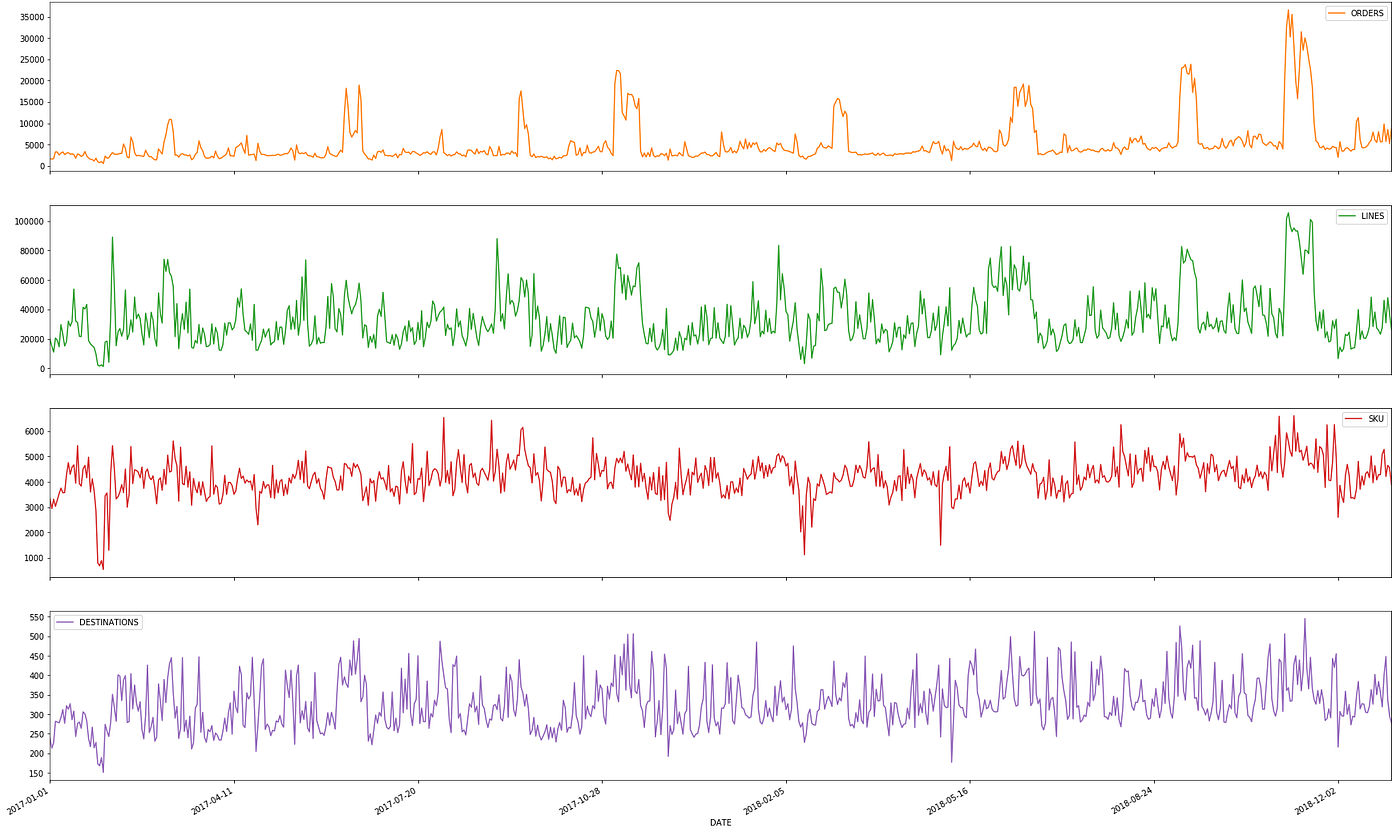
In the example below, you can see the daily variation of key indicators that will drive your workload (#Orders, #Lines, #SKU, …).
From one day to the next, you can see significant variation that your teams need to absorb.
Given that your workers' average productivity is stable, the only solution is to adapt your resources to meet daily demand.
💌 New articles straight to your inbox for free: Newsletter
Workforce Planning: Problem Statement
Scenario
You are an Inbound Manager of a Distribution Centre operated by a Third Party Logistics Company (3PL) for a large retailer.
Your team's responsibilities include
- Unload Pallets from the Trucks
- Scan each pallet and record the received quantity in your Warehouse Management System (WMS)
- Put away these pallets in the Stock Area
The team’s global productivity is measured each week in (Pallets/Hour).
At the beginning of each month, your colleagues from the transportation team share a forecast of the number of pallets to be received every day for the next 4 weeks.
If you prefer watching, here is the video version
Workforce Sizing
Based on these forecasts and your global productivity, you can estimate what resources would be needed each day

For more flexibility, you will use 100% of temporary workers to build your team.
Constraint 1: The Supply must meet the demand
If you need 31 workers on Monday, you must secure at least 31 for Monday.
Constraint 2: Minimum working time by worker
To ensure employee retention, you need to guarantee at least five consecutive working days per week.
Workforce sourcing can be challenging, especially if e-commerce fulfilment centres surround your DC.
Therefore, you need to ensure a minimum number of working hours for your temporary workers to remain attractive employers.
Constraint 3: Maximum working time by week
In accordance with local regulations, each worker must rest for 2 days after 5 consecutive working days.

A worker from Shift 1 will start his week on Monday and get 2 days off on Friday.
Her colleague from Shift 6 will start the week on Saturday and get 2 days off on Thursday.
Objective: Minimise the number of workers hired
In line with your manager's productivity targets, you must minimise the number of workers hired.
If you do not meet this target, your P&L may be affected, as this productivity was used to calculate the price invoiced to your customer (retailer).
Linear Programming Problem
We define a Linear Programming Problem by
- Finding the optimal value of a linear function: objective function
- By selecting the right decision variables (x[i])
- Subject to the conditions that the variables are non-negative and satisfy a set of linear inequalities called constraints
Our problem fits perfectly!
x[i]: number of temporary workers hired for shift i
Constraints
For each day, the total number of workers on duty must be higher than the demand
- Each worker needs to work a minimum of 5 consecutive days per week
- Each worker needs to have 2 days off after 5 consecutive days of work
Objective functions
The total number of temporary workers hired for all shifts i = 1 … 7 should be minimal
Linear Programming with PuLP
PuLP is a modelling framework for Linear (LP) and Integer Programming (IP) problems written in Python.
Prepare your parameters
- Create a circular list for the days
If you add 5 days to Friday, you will reach Wednesday - List of Working Days:
If day = 0 (Monday), then working days are Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday and Friday - Workers off by shift for each day:
If day = 0 (Monday), then workers of shift 2 (Starting Tuesday) and shift 3 (Starting Wednesday) are off
Initialise the model, define the objective and add constraints
- Initialise Model “Minimise Staffing” to minimise the objective
- Create variables x[i]: number of workers hired for shift i
- Define objective: sum of workers hired x[i]
- Add constraints: the sum of workers on duty (not on a day off) is higher than the minimum staff demand
Solve your model and analyse the results
Results: Number of workers hired?
Total number of Staff = 53
Insights
0 workers hired for Thursday and Saturday shifts
Supply vs. Demand: What is the gap?
Do we have more workers than needed?
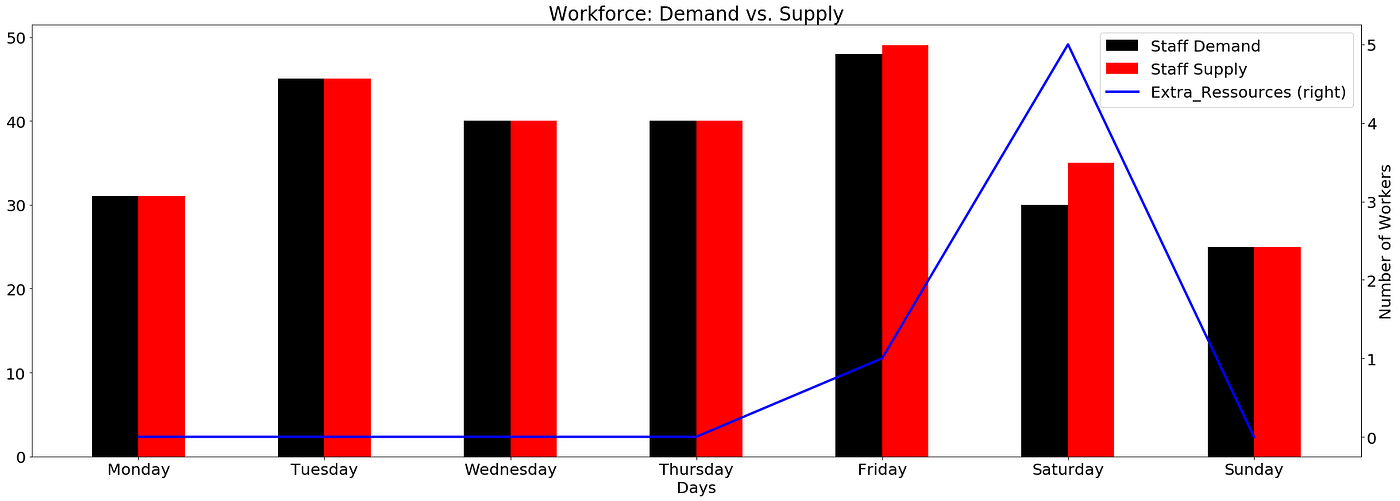
Insights
Friday: 1 extra worker
Saturday: 5 extra workers
The implementation is available on my GitHub.
Conclusion
Our results respect the constraints, i.e. the demand is met.
However, this sizing is not satisfactory, as we have six extra man-days to add to our P&L due to Friday and Saturday.
Improve the simulation
Try to influence several parameters
- The 2-day-per-week constraint?
- What is the constraint of having consecutive days of work?
- What is the constraint of having a minimum of 5 days worked per week?
You can try these scenarios and share your results (or questions) in the comment section.
What about improving the productivity?
In this exercise, we focus solely on workforce allocation, treating productivity as a fixed parameter.
We can do better than this.
Here are some inspirations for you,

About Me
Let’s connect on LinkedIn and Twitter. I am a Supply Chain Engineer using data analytics to optimise logistics operations and reduce costs.
If you’re looking for tailored consulting solutions to optimise your supply chain and meet sustainability goals, feel free to contact me.