Green Inventory Management for Fashion Retail - Case Study
Discover how to reduce the CO2 footprint of fashion retail logistics by implementing green inventory management practices. Learn how to reduce store deliveries and cut carbon emissions. Read more now.
Green inventory management can be defined as managing inventory in an environmentally sustainable way.
This story has been originally published on Medium.
For the distribution network of a Fashion Retail company, this can involve a set of processes and rules that aim to reduce the environmental impact of order transmission, preparation and delivery.
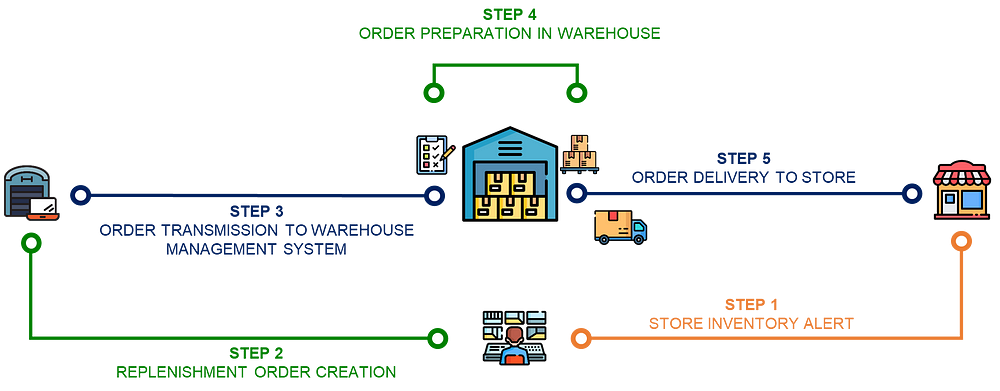
For most retailers, inventory management systems take a fixed, rule-based approach to manage the frequency of store replenishment (and quantity) to ensure that stores’ inventory can cover the demand.
In this article, we will use data analytics to simulate the variation of store replenishment frequency and measure the impact on the overall environmental impact.
I. Scenario
1. Inventory Management for Retail
Manage store inventory using a periodic review policy.
2. What if we change the review period?
Impacts on truck filling rates and the percentage of mixed cartons.3. What are the impacts on CO2 emissions?
II. Experiment
1. Simulation Model
Simulate inventory management and warehouse operations.
2. Scenarios
Results for review periods between 2 and 10 days.
III. Results
1. Impact on Transportation emissions
Fewer deliveries and higher fill rate = CO2 emissions reductions
2. Carton Material Usage
Fewer mixed cartons = less carton material used3. Productivity & Social ImpactsHigher productivity = higher bonus for operatorsIV. Conclusion
Scenario
Inventory Management for Retail
You support the inventory manager of a mid-size fashion retail chain; he is in charge of setting the replenishment rules in the ERP.

You have implemented a periodic review policy Order-Up-To-Level (R, S)
- Your ERP is reviewing stores’ inventory levels (also called inventory on hand) every R days: IOH
- For each review, the gap between the inventory level and the target inventory S is calculated: S— IOH
- A Replenishment Order is created and transmitted to the warehouse with the quantity: Q = S — IOH
The idea is to deliver the missing quantity to reach this target level.

After transmission, the order is prepared at the warehouse and delivered to your store after a certain lead time LD (days).
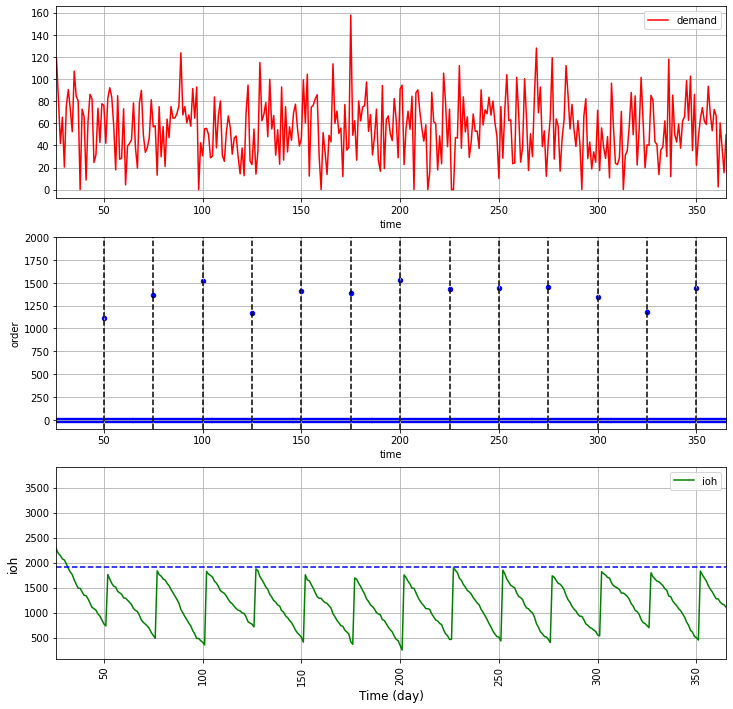
You should set the target stock to absorb the demand variability and the replenishment lead time so your inventory remains positive until your order is delivered.

For more details, you can have a look at this article
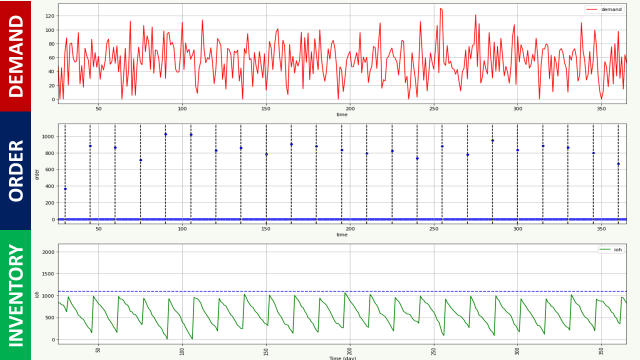
What if we change the review period?
The review period is setting the frequency of store replenishment order creation.
- For R = 2 days, your store is replenished frequently, so you can set a lower target stock level to cover the demand during the review period.
- R = 15 days, the order quantity per replenishment is higher as your target stock level needs to absorb the demand during a longer review period.
What are the impacts on CO2 emissions?
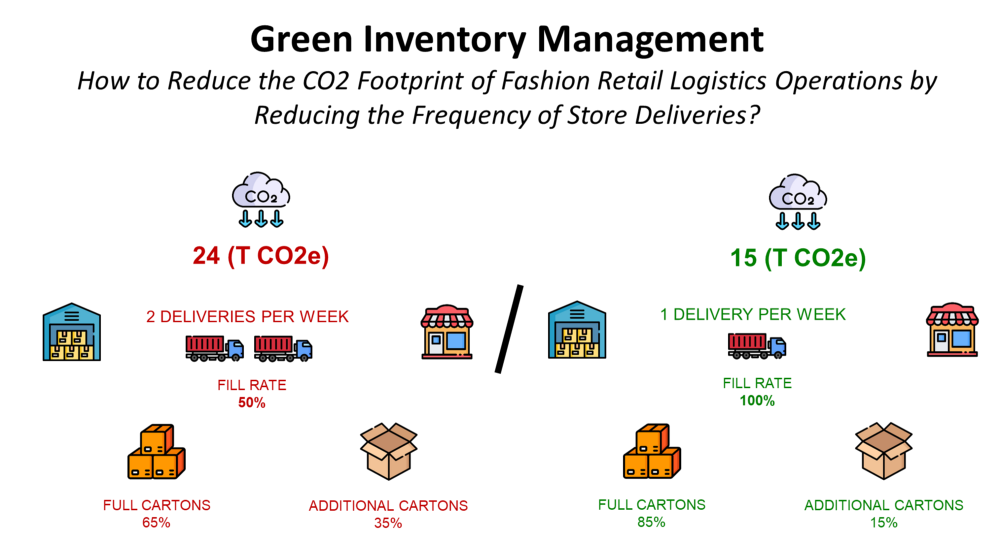
On the left side, we can see that we have more store deliveries (with a lower quantity per shipment) for the same time duration.
Impact on the carton usage
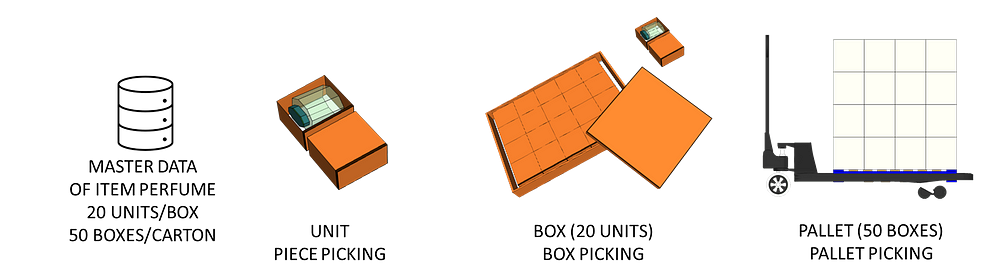
Items are received in cartons containing units that can be picked individually.
If the order quantity is five, the operator will
- Open a box of 20 units and take five units;
- Take a new box and put these ,;
- Complete the box with other items ordered by the store
The total number of mixed cartons can be easily computed using the formula below.
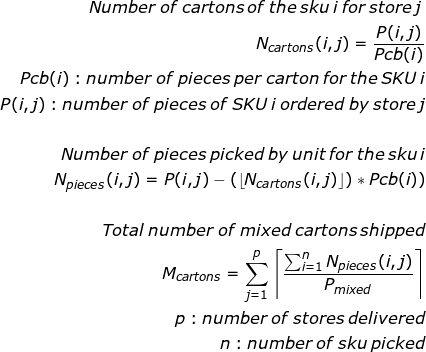
These boxes (or mixed cartons) will require additional packing material that will impact your footprint.
With a high frequency, the quantity per replenishment is reduced, and this situation can occur more.
Impact on transportation emissions
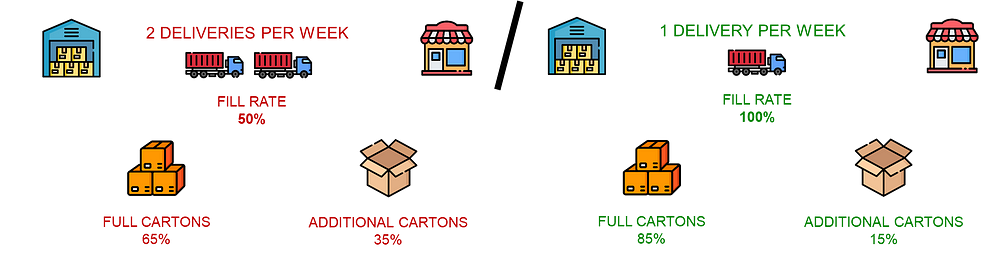
The review period can also impact the number of deliveries during a certain period.
If you double the delivery frequency, you reduce the number of pallets per truck and impact the filling rate.
Thus, you may have to travel more distances (and use more fuel) to replenish the same quantity of goods The numberin the stores.
Experiment
Simulation Model
We will take the example of a logistic network that replenishes 10 fashion retail stores in the region of Shanghai (PRC).
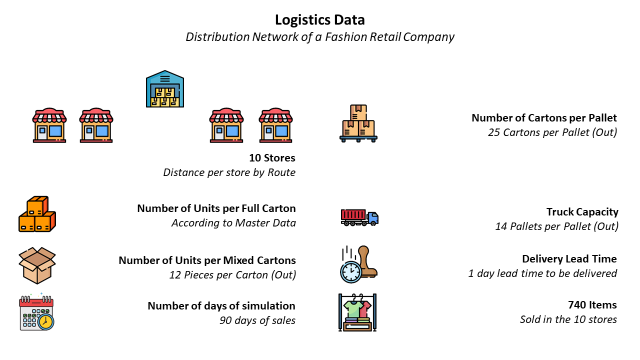
In this simulation, we will consider
- 90 days of sales of 10 stores located around the warehouse
- 740 unique items (SKU) sold in these 10 stores
- The number, of units per full carton provided by the master data
- 12 pieces per mixed carton
- 1 day lead time between order creation and store delivery
Based on these parameters, we can estimate the filling rates of trucks and the number of additional boxes needed. [Ref. 1, Ref. 2]

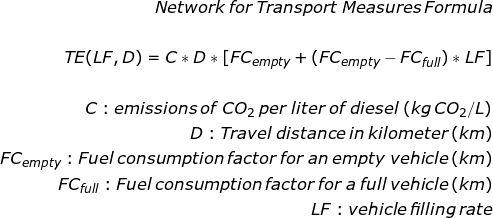
We can then estimate the environmental impact using the following parameters,
- CO2 emissions of trucks are estimated using the NTM (Network for Transport Measures) methodology with the transportation distance and emissions factors
- Based on the mixed carton dimension and thickness, we can estimate the quantity of material per carton
💡 Insights
- NTM methodology can help us,consider the impact of the truck filling on your overall emissions
- To improve the model, we can also consider the filling material (in your mixed cartons) and the wrapping film on your pallets.
Scenarios
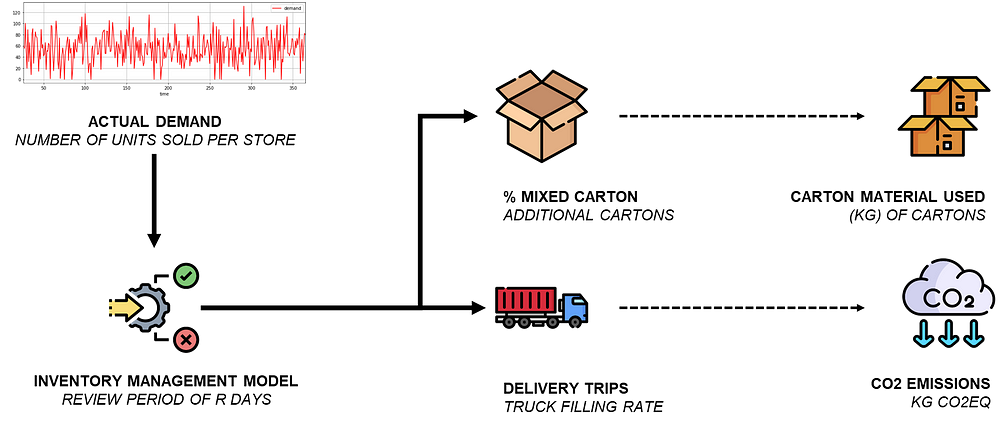
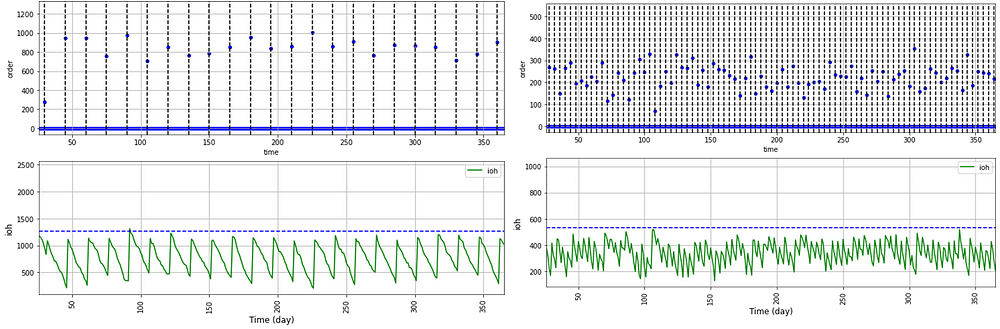
We will simulate the overall emissions and carton material usage considering a review period going from 2 to 10 days.
For each scenario, we will look at
- The percentage of mixed cartons prepared (%)
- The total quantity of carton material used to prepare these mixed cartons (kg)
- The percentage of partially filled trucks used to deliver the stores (%)
- The total CO2 emissions of road transportation (kg CO2eq)
Results
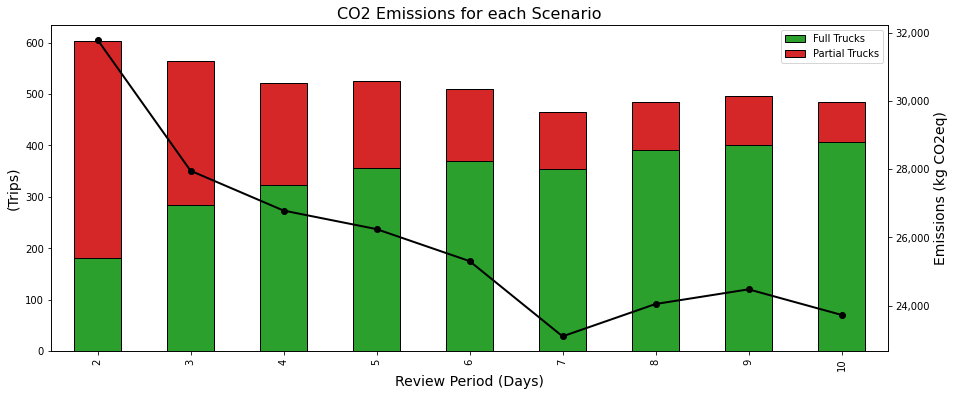
Transportation Emissions
The initial assumption was that a lower delivery frequency would improve the filling rate of trucks and reduce emissions.
This is confirmed by the simulation results below.
💡 Insights
- The minimum number of trips is reached for a review period of 7 days
- -27% of emissions between Scenario 1 (R =2) and Scenario 6 (R = 7)
- -51% of trips between Scenario 1 (R =2) and Scenario 6 (R = 7)
As we can see, emissions are increasing for R >7, and it seems that the optimal rule potentially matches the demand for a weekly seasonality.
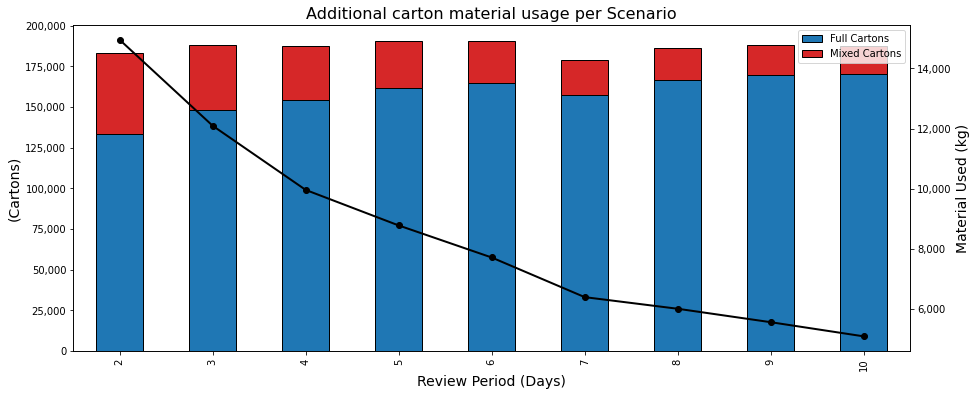
Carton Material Usage
For each scenario, we count the number of mixed cartons we need to prepare to fulfil the replenishment orders.
With a lower frequency of orders, we are supposed to increase the quantity per order and reduce the percentage of items picked by piece.
💡 Insights
- Without surprise, the total number of cartons prepared remains stable as the total demand during the simulation period remains the same for all scenarios.
- The percentage of mixed cartons is dropping from 27% (Scenario 1: R = 2) to 9% (Scenario 9: R = 10)
- -65% of carton usage between Scenario 1 (R= 2) and Scenario 9 (R= 10)
Productivity & Social Impact
In a Distribution Center (DC), walking time from one location to another during the picking route can account for 60% to 70% of the operator’s working time.
A major parameter influencing your operators' productivity is the number of cartons picked at each location.
Their productivity is measured by the number of cartons picked per hour paid.
And they can receive bonuses added on top of their base salary if they achieve their targets.
For example, with a target of 200 boxes/hour, the operator will need less effort to reach if he takes four cartons per stop than two cartons per stop.

💡 Insights
- +65% full cartons per replenishment order line
- Operators will prepare on average +2.07 boxes more for the same picking route distance.
This will reduce your human resources variable costs and help operators reach their targets with less effort.
Drawbacks: average store inventory level
As nothing is perfect, there are some drawbacks to increasing the review period.
When you have a lower replenishment frequency, you need to increase the stock coverage in your stores.
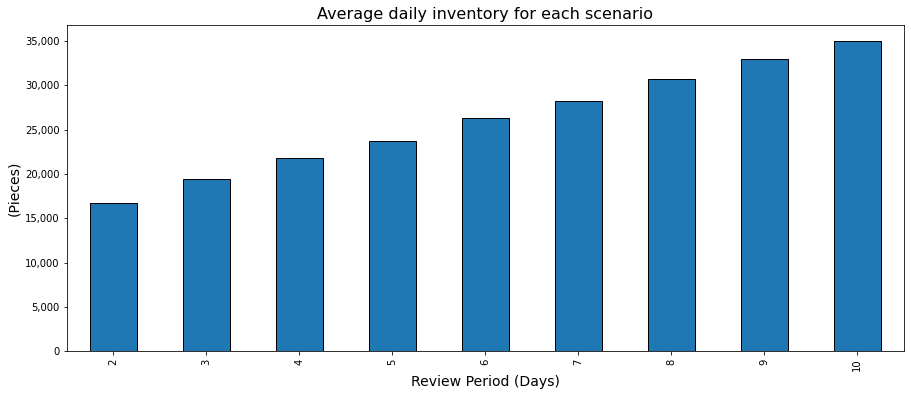
💡 Insights
- +108% of average inventory for all stores between Scenario 9 (R = 10) and Scenario 1 (R = 1)
That means you will need additional space for storage in your stores.
Conclusion
A balanced approach is needed
Like everything in Supply Chain Management, it is a matter of balance.
Depending on the cost per sqm in your store locations, you can allocate more or less space for storage.

However, this additional cost should be put into perspective with the potential savings of warehousing and transportation.
Improve the simulation
If you need additional savings to convince your management, you can improve the model by bringing additional savings calculation.
- Goods handling processes in the warehouse: picking locations replenishment, truck loading, carton packing
- Receiving at the store: truck unloading,
- Packing Material: filling material, labels, pallet wrapping
You can compare the ratio of emissions reductions by euro invested with other green solutions like e-trucks, renewable energy or recycled packing material.
About Me
Let’s connect on Linkedin and Twitter, I am a Supply Chain Engineer using data analytics for supply chain optimization, sustainability and personal productivity.
If you’re looking for tailored consulting solutions to optimize your supply chain and meet sustainability goals, feel free to contact me.